What is Urbanisation?
What is Urbanisation?
Cities are facing unprecedented demographic, environmental, economic, social and spatial challenges.
There has been a phenomenal shift towards urbanization, with 6 out of every 10 people in the world expected to reside in urban areas by 2030. Over 90 per cent of this growth will take place in Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean.
In the absence of effective urban planning, the consequences of this rapid urbanization will be dramatic.
In many places around the world, the effects can already be felt:
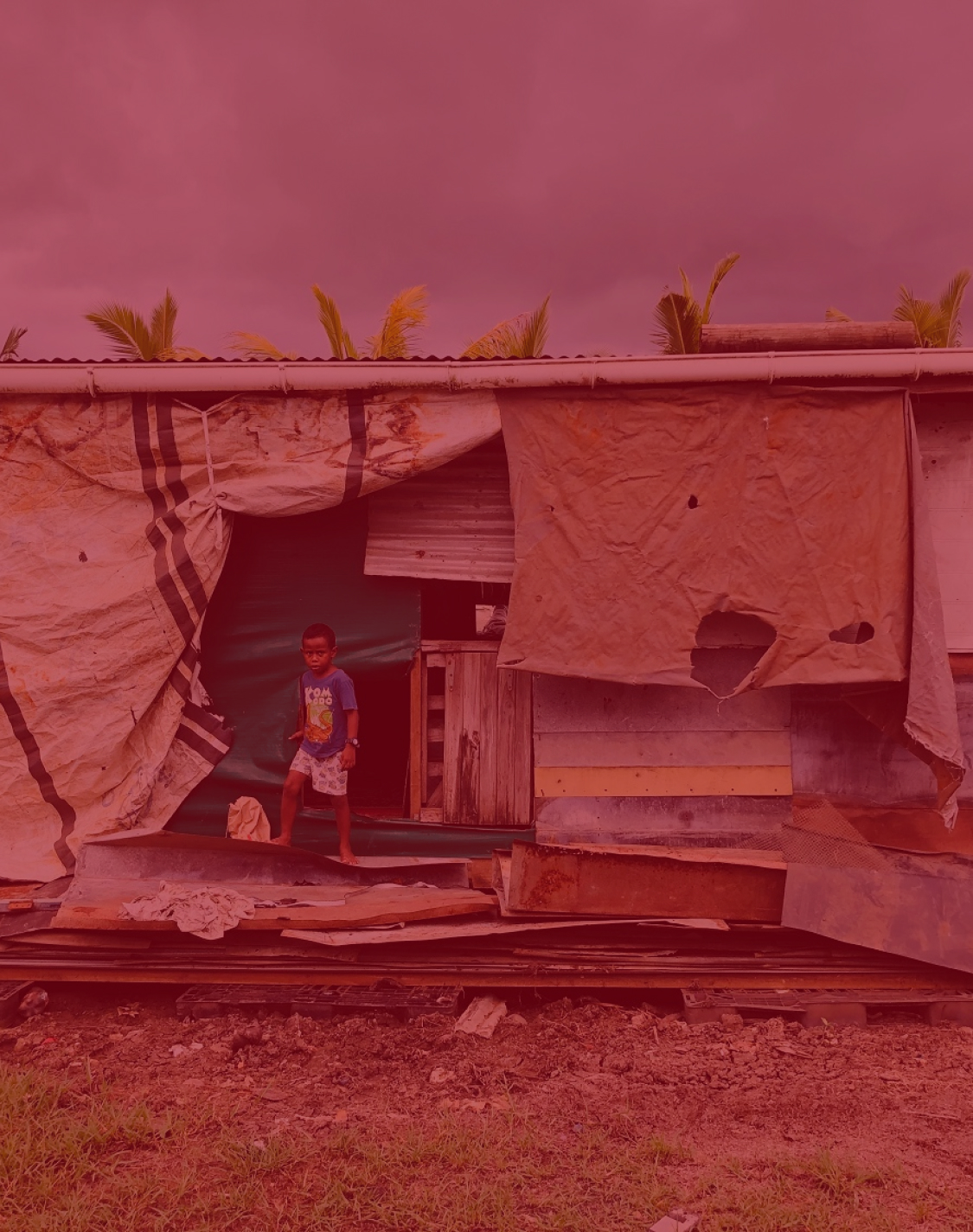
lack of proper housing and growth of slums, inadequate and outdated infrastructure – be it roads,
public transport, water, sanitation, or electricity – escalating poverty and unemployment, safety and crime problems, pollution and health issues, as well as poorly managed natural or man-made disasters and other catastrophes due to the effects of climate change.
Mindsets, policies, and approaches towards urbanization need to change in order for the growth of cities and urban areas to be turned into opportunities that will leave nobody behind. UN-Habitat, the United Nations programme for human settlements, is at the helm of that change, assuming a natural leadership and catalytic role in urban matters.








Sustainable Cities and Communities
Half of the world’s population now live in cities, and this is projected to increase to two-thirds by 2050. Cities can solve many of the challenges our world faces. Urban areas drive innovation, consumption and investment worldwide, making them a positive and potent force for addressing sustainable economic growth, urban development and prosperity.
No Poverty
With humanity becoming increasingly urban, trends indicate poverty is also becoming increasingly urban. Sustainable urbanisation improves the lives of people in human settlements around the world and increases prosperity.
Zero Hunger
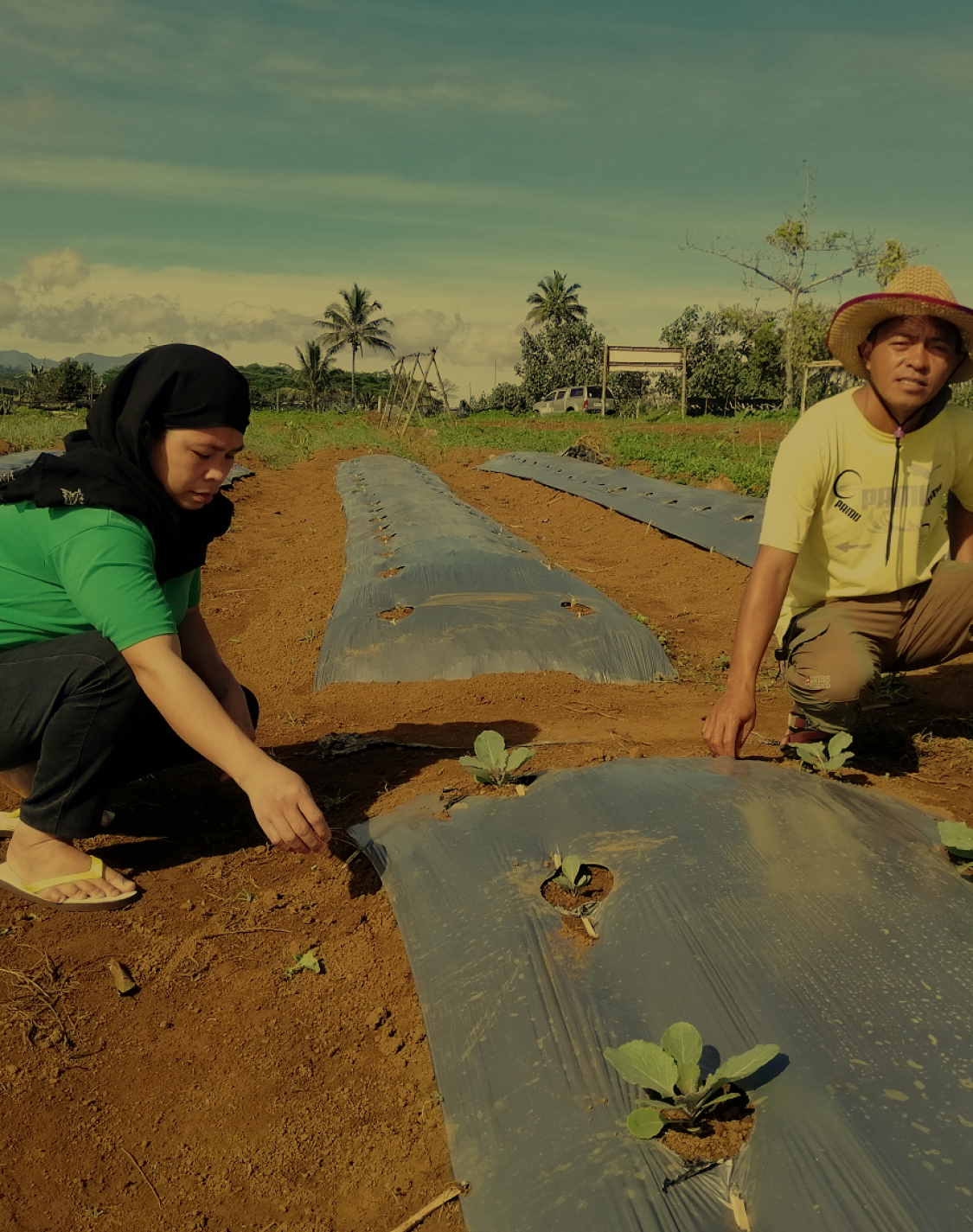
Sustainable urbanisation increases food security. The presence of cultivable land for farming provides food for urban areas and supports agricultural productivity whilst improving the livelihoods of rural populations.
Good Health and Well-Being
Through integrated urban planning, access to basic services, and access to decent and affordable housing, sustainable cities contribute to better health.
Quality Education
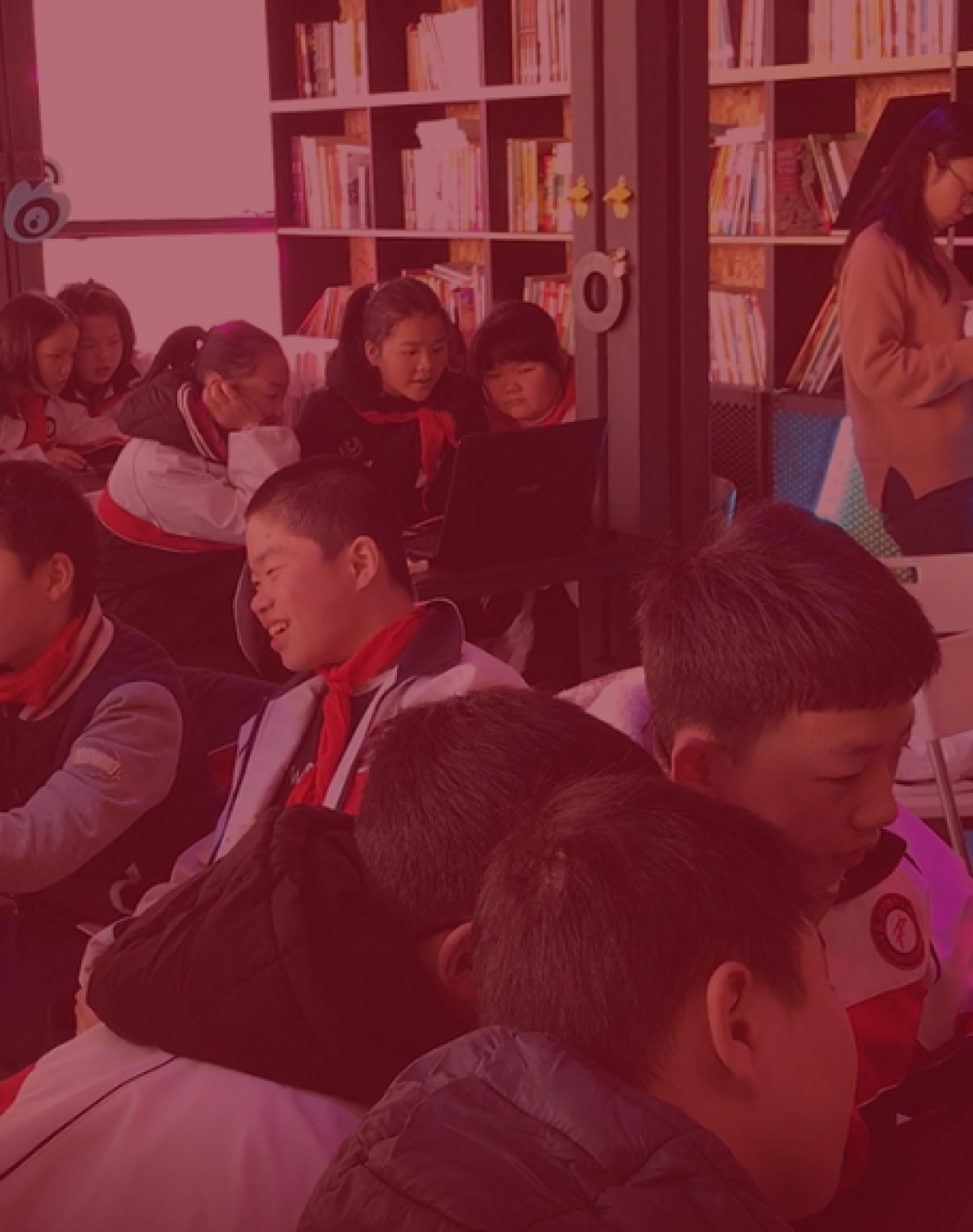
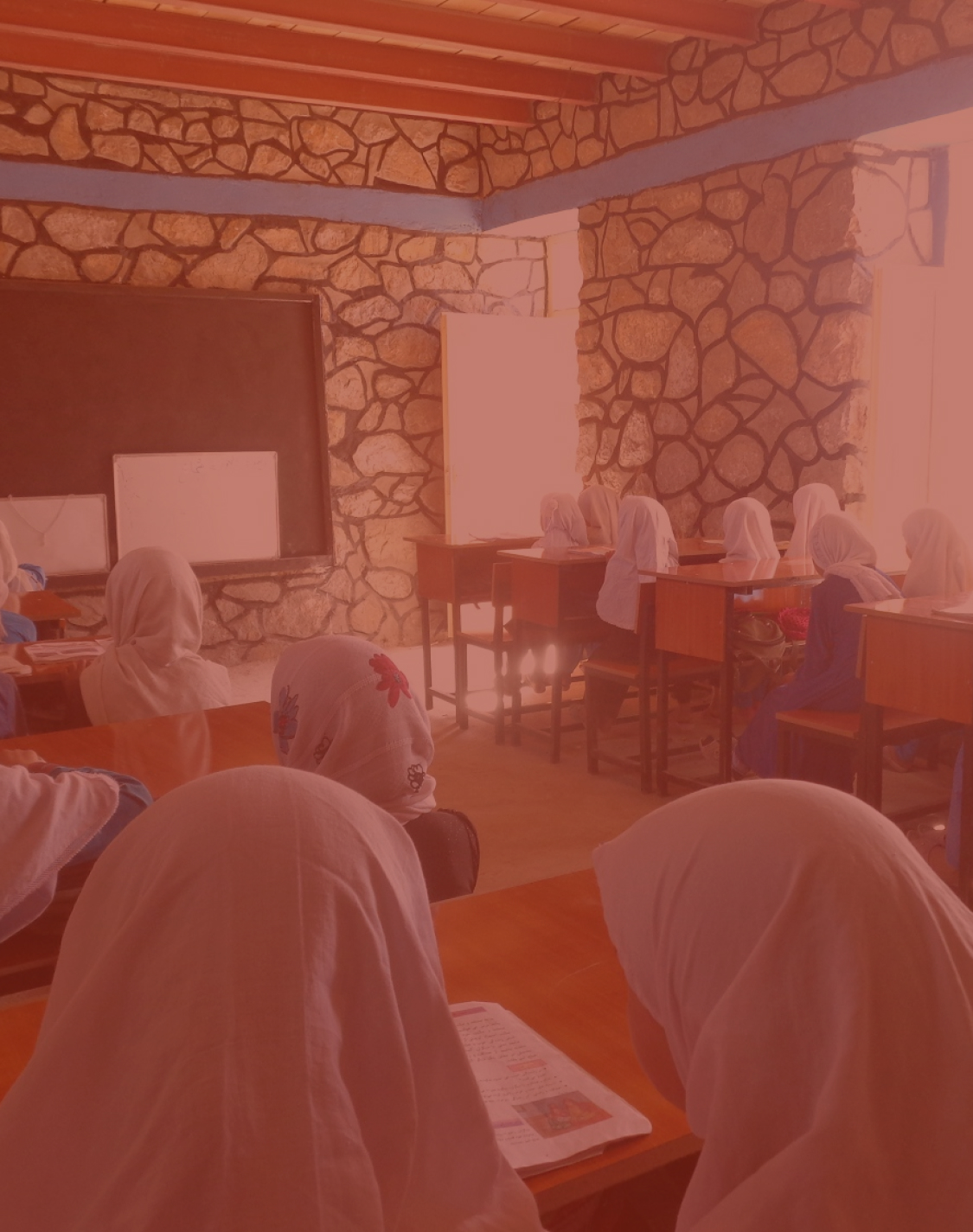
Inclusive and sustainable cities provide better access to education by the urban poor, women and girls. Inclusive and equitable education provides adequate skills for decent jobs and improved living conditions.
Gender Equality
Providing women and girls with equal access to education, health care, decent work, and representations in political and economic decision-making processes nurtures sustainable economies, and helps develop inclusive and sustainable cities.
Clean Water and Sanitation
Effective urban planning and urban water management systems ensure access to safe drinking water, sanitation and hygiene, and improve the quality and sustainability of water resources worldwide.
Affordable and Clean Energy
Access to clean and efficient energy systems is crucial for development of safe, resilient and sustainable cities, allowing them to grow and perform efficiently while reducing pollution and mitigating climate change.
Decent Work and Economic Growth
Inclusive and sustainable cities are a positive and potent force for addressing sustainable economic growth and prosperity, as they drive innovation, consumption and investment.
Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
Investment in infrastructure, industrialization and innovation are key to making cities safe, resilient, inclusive and sustainable.
Reduced Inequalities
Sustainable cities address prevailing inequalities through better urban planning, design and governance, providing better opportunities for employment, affordable housing and accessible transport.
Sustainable Cities and Communities
Half of the world’s population now live in cities, and this is projected to increase to two-thirds by 2050. Cities can solve many of the challenges our world faces. Urban areas drive innovation, consumption and investment worldwide, making them a positive and potent force for addressing sustainable economic growth, urban development and prosperity.
Responsible Consumption and Production
Sustainable urbanisation uses natural resources innovatively and efficiently. These sustainable patterns of production and consumption increase cities productivity and reduce negative environmental impacts.
Climate Action
Sustainable cities provide real opportunities to mitigate and adapt to the effects of climate change, through environmentally sustainable and resilient urban design, development and governance.
Life Below Water
Sustainable urban planning and proper management of resources can reduce the pressure coastal cities put on the environment. Proper management of waste generated by cities prevents ocean pollution and protects biodiversity.
Life on Land
Sustainable urbanisation and better urban planning, including the development of green infrastructures and the safe management and treatment of waste, can conserve and restore terrestrial ecosystems.
Peace and Justice and Strong Institutions
Peaceful, inclusive and sustainable cities rely on the kind of institutions we build in cities. This impacts how we govern our cities as well as how we implement the process of urbanisation itself.
Partnerships for the Goals
Increasing international cooperation is seen as vital to achieving each of the 16 previous goals. Achieving the SDGs, including Goal 11, will only be possible if there are strong partnerships within and across with all the goals.
The SDGs are based on the spirit of partnership and pragmatism,
and aim to sustain and improve the lives of future generations by making the right choices now.
UN-Habitat’s Goal - SDG11 “Sustainable Cities and Communities”
UN-Habitat’s Goal - SDG11 “Sustainable Cities and Communities”

Since 2007, more than half of the world's population has been living in cities.
By 2030, this share is expected to reach 60%. Cities and metropolitan areas are the engines of economic growth, accounting for about 60% of the world's GDP.
However, cities are responsible for about 70% of the world's carbon emissions and more than 60% of the world's resource use. Rapid urbanization has led to an increase in the number of slum dwellers, unplanned urban expansion, climate change, and inadequate and overburdened infrastructure and services (waste collection, water and sanitation systems, roads and transportation, etc.)
Furthermore, the impacts of COVID-19 will be most devastating in densely populated and poor urban areas, especially for the world's one billion people living in informal settlements and slums. Overcrowding makes it difficult to take recommended measures such as social distancing and self-isolation, and lack of adequate services puts vulnerable communities at a serious disadvantage.
SDG 11 Target Goals for 2030
SDG 11 Target Goals for 2030
Everyone can help to make sure that we meet the Global Goals.
Use these ten targets to create action to make cities and communities sustainable.

By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services and upgrade slums.

By 2030, provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all, improving road safety, notably by expanding public transport, with special attention to the needs of those in vulnerable situations, women, children, persons with disabilities and older persons.

By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries.

Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage.

By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease the direct economic losses relative to global gross domestic product caused by disasters, including water-related disasters, with a focus on protecting the poor and people in vulnerable situations.

By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management.

By 2030, provide universal access to safe, inclusive and accessible, green and public spaces, in particular for women and children, older persons and persons with disabilities.

Make cities and
human settlements
inclusive,safe,
resilient and
sustainable
Make cities and
human settlements
inclusive,safe,resilient and
sustainable
What You Can Do to Help

Share on Social Media
Are you familiar with the phrase, “sharing is caring”?
In this case, it truly is. Raising awareness around urbanisation issues,
and the activities of UN-Habitat can help raise funds and support from organisations.
Sharing on social media is the easiest way to get involved,
and is just as valuable as donating or volunteering!
Your one shared post can have a tremendous impact, even if you don’t realise it.

Join our Events
Do you feel a social responsibility, but don't know where to start?
A great way to learn more about urbanisation issues and support UN-Habitat is by participating in events. Many of our events are online, so you can join from anywhere in the world.
Check out our events - from kids to adults to professionals, there is something for everyone.

Become a Partner
Tackling some of the toughest global challenges cannot be accomplished by one company or one organization alone. By working together, we can make a greater impact. In order to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals and implement projects, governments, civil society, scientists, academia, and the private sector must work together. UN-Habitat is built on strong, inclusive and integrated partnerships at all levels to implement our commitments and put them into action. Through partnerships, the reach and unique capabilities of our partners can make them a powerful source of innovation and execution. We’re all in this together.